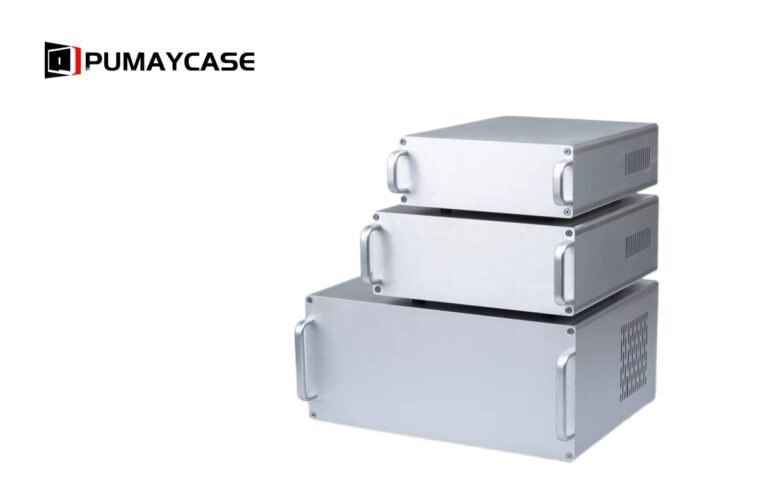
Enclosures in high-temperature environments face unique challenges such as overheating, material degradation, and reduced performance. A well-designed enclosure can prevent these issues and protect sensitive components.
For high-temperature applications1, selecting the right materials, ventilation design2, and thermal management3 is essential.
Here’s a guide on how to design an enclosure that performs reliably in extreme heat.
What Materials Are Best for High-Temperature Enclosures?
The material of the enclosure plays a significant role in heat resistance.
Aluminum is a popular choice due to its excellent heat dissipation and durability.4 However, alternative materials may be used depending on the application.
- Aluminum (6063, 5052): Offers high thermal conductivity, lightweight, and good corrosion resistance.
- Stainless Steel5: Provides superior strength and high-temperature resistance but is heavier and more expensive.
- High-Temperature Plastics (Polycarbonate, ABS with heat additives)6: Suitable for non-metal applications up to certain temperature limits.
Material Comparison for High-Temperature Environments
| Material | Max Temperature | Thermal Conductivity | Weight | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 660°C | Excellent | Light | Moderate |
| Stainless Steel | 1500°C | Moderate | Heavy | High |
| Polycarbonate | 120°C | Low | Light | Low |
How to Improve Heat Dissipation in Enclosure Design?
Efficient heat management is critical for high-temperature applications.
Incorporating heat-dissipating features7 in the enclosure can significantly reduce internal temperature.
Key Design Features for Heat Dissipation:
Ventilation Openings8\
Add strategically placed vents to allow natural airflow and prevent heat buildup.Heatsinks9\
Use external heatsinks to increase surface area and improve thermal dissipation.Thermal Insulation10\
For sensitive components, use insulating materials to protect against extreme heat.Forced Cooling\
For more demanding applications, integrate cooling fans or heat exchangers.
What Surface Treatments Are Suitable for High-Temperature Enclosures?
The right surface treatment can enhance the enclosure’s heat resistance and longevity.
Anodizing11 is an excellent choice for aluminum enclosures in high-temperature environments. It provides a protective layer that improves heat resistance and prevents oxidation.
Other options include:
- Ceramic Coating12: Offers superior heat resistance for extreme conditions.
- High-Temperature Paint: Provides protection and aesthetic appeal up to specific temperature limits.
How to Test an Enclosure for High-Temperature Reliability?
Testing is essential to ensure the enclosure can withstand high temperatures without failure.
- Thermal Cycling Test13: Simulates rapid temperature changes to test durability.
- Constant Temperature Test14: Verifies performance under prolonged high-temperature exposure.
- Component Functionality Test15: Ensures that sensitive components continue to function within acceptable limits.
What Applications Require High-Temperature Enclosures?
High-temperature enclosures are essential in industries such as:
- Industrial Automation: Protects control systems in harsh factory environments.
- Power Electronics: Prevents overheating in power converters and inverters.
- Aerospace and Defense: Ensures reliability in extreme atmospheric conditions.
Designing an enclosure for high-temperature environments requires careful selection of materials, heat management strategies, and reliable surface treatments. With the right approach, you can ensure your enclosure remains durable and functional in even the most extreme conditions.
Understanding best practices can help you design enclosures that withstand extreme heat effectively. ↩
Learning about ventilation strategies can prevent overheating and ensure optimal performance of your enclosures. ↩
Exploring thermal management techniques can enhance your enclosure's reliability and longevity in harsh conditions. ↩
Explore the advantages of aluminum in heat management, including its durability and efficiency in various applications. ↩
Discover the unique properties of stainless steel that make it suitable for high-temperature environments and its advantages over other materials. ↩
Learn about high-temperature plastics and how they can be effectively used in applications requiring heat resistance. ↩
Understanding heat-dissipating features can help you design better enclosures for high-temperature applications. ↩
Explore how ventilation openings can enhance airflow and prevent overheating in various applications. ↩
Learn about the role of heatsinks in increasing surface area for better heat management in electronic devices. ↩
Discover the best insulating materials to protect sensitive components from extreme heat. ↩
Explore the advantages of anodizing to understand how it enhances heat resistance and longevity for aluminum enclosures. ↩
Learn about ceramic coating's superior heat resistance and its applications in extreme conditions. ↩
Understanding Thermal Cycling Tests can help you ensure the durability of enclosures in extreme conditions. ↩
Exploring Constant Temperature Tests will provide insights into maintaining performance under heat stress. ↩
Learning about Component Functionality Tests is vital for ensuring the reliability of sensitive components in high temperatures. ↩