Enclosure design demands precision. Picking the wrong aluminum processing method can lead to wasted time, higher costs, and failed prototypes. How do engineers decide?
The best aluminum processing method depends on your project's complexity, volume, budget, and precision needs. Common options include extrusion, CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication (bending/cutting), and casting. Each works for different situations.
%[aluminum enclosure fabrication methods]( "Common aluminum processing techniques")
"Common aluminum processing techniques")
Understanding aluminum processing isn’t just about picking a technique—it’s about matching your project’s needs to the fastest, most cost-effective solution. Let’s break down the key methods.
What Are the Processing Methods for Aluminum?
Aluminum enclosures require shaping raw metal into protective shells. But with so many techniques available, where should you start?
Aluminum processing includes extrusion (pushing heated metal through dies), CNC machining (precision cutting), sheet metal work (bending/cutting), casting (pouring molten metal into molds), and welding/joining methods like TIG or MIG for assembly.
%[aluminum processing flow chart]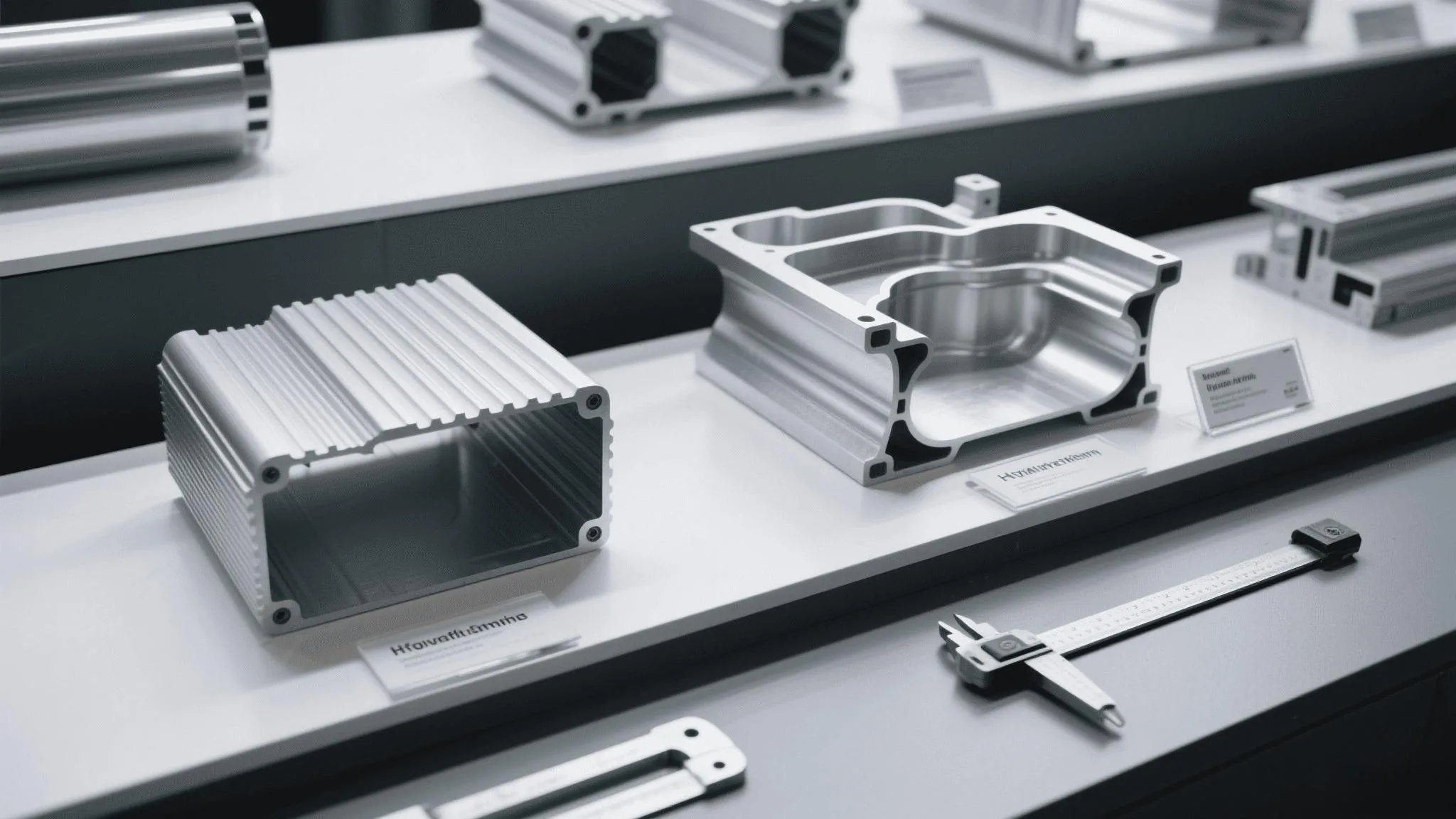 "From raw aluminum to finished enclosure")
"From raw aluminum to finished enclosure")
Key Methods Compared
| Method | Best For | Speed | Cost (Low→High) | Precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extrusion | Standardized shapes | Fast | $ | Medium |
| CNC Machining | Complex/custom parts | Slow | $$$ | High |
| Sheet Metal | Thin, flat components | Medium | $$ | Medium |
| Casting | Large, simple parts | Very slow | $$$$ | Low |
Extrusion suits mass production of uniform profiles (e.g., server racks). CNC machining is ideal for prototypes or high-tolerance parts (sensor housings). Sheet metal balances cost and flexibility for covers/panels. Casting is rare in electronics due to rough surfaces and porosity risks.
What Is the Most Common Method Used for Joining Aluminum Sheets Together?
Durable enclosures need strong joints. But aluminum’s heat sensitivity makes bonding tricky. Which joining method prevents leaks and cracks?
For thin aluminum sheets (≤3mm), riveting or clinching offers quick, tool-free assembly. Thicker sheets (≥5mm) often use TIG welding for airtight seams. Adhesives work for non-structural panels needing vibration resistance.
When to Use Each:
- Riveting: Field repairs/IP54-rated outdoor boxes (no heat distortion).
- TIG Welding: IP67+ enclosures (medical/automotive). Requires skilled labor.
- Adhesives: Lightweight drones/consumer devices. Avoid for load-bearing parts.
Pro tip: Anodized aluminum resists corrosion but requires special welding wire (4043 alloy) to prevent joint brittleness.
What Are the Different Types of Aluminum Fabrication?
"Fabrication" covers all processes that transform raw aluminum into functional parts. Which ones fit electronics enclosures?
Aluminum fabrication includes subtractive (CNC milling), formative (bending), additive (3D printing), and joining methods. Most enclosures combine techniques—e.g., extruded bases + laser-cut panels + welded seams.
%[fabrication workflow example](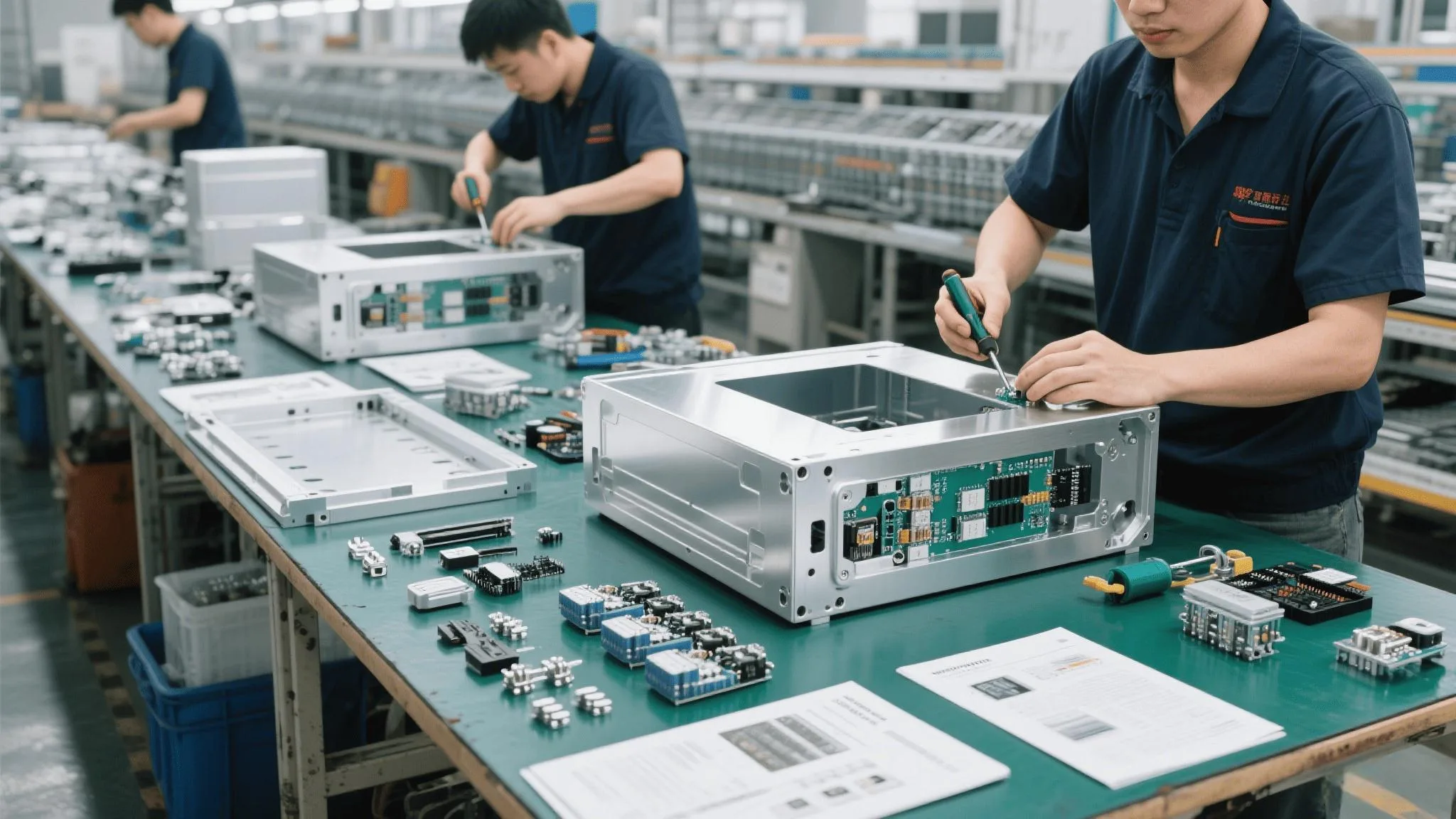 "From CNC machining to final assembly")
"From CNC machining to final assembly")
Practical Workflows:
- Low Volume: CNC all parts from solid blocks (high waste but no tooling costs).
- Medium Volume: Laser-cut sheets + brake press bends (faster, ≤5mm thickness).
- High Volume: Custom extrusion dies + robotic welding (low per-unit cost).
At PUMAYCASE, we use modular extrusion profiles to cut clients’ lead times—pre-made grooves for gaskets eliminate secondary machining.
What Processes Form Aluminum into Shapes We Can Use?
From industrial servers to handheld devices, aluminum shapes vary wildly. How do factories produce these forms efficiently?
Aluminum shaping starts with primary processes (extrusion/rolling for basic forms) and finishes with secondary machining (drilling/tapping). Modern techniques like hydroforming create complex curves without welds.
%[aluminum shaping stages] "Extrusion vs. hydroforming examples")
"Extrusion vs. hydroforming examples")
Cost vs. Complexity:
- Extruded Channels: Simple, $0.50–$5 per linear foot.
- CNC’d Enclosures: $100–$500 per unit (5-axis machines).
- Hydroformed Housings: $1,000+ for molds but zero assembly seams.
For one aerospace client, we replaced 6 welded pieces with a single hydroformed shell—reducing weight by 15% and assembly time by 8 hours.
Conclusion
Choose aluminum processing based on volume, precision, and budget. Combine methods like extrusion + CNC for enclosures that are fast to produce yet custom-fit. Need guidance? Let’s talk.